In Singapore, data security is not just a technical requirement but a strategic advantage. Frameworks such as the PDPA, MAS TRM Guidelines, and CSA’s Cyber Essentials & Trustmark align closely with ISO/IEC 27001, the most widely recognised international standard for creating and preserving an Information Security Management System (ISMS).
By adopting ISO 27001, organisations can demonstrate compliance, strengthen customer trust, and compete confidently in today’s digital economy. With rising regulatory expectations and growing cyber threats, SMEs and startups that embrace ISO 27001 are better positioned to protect data and achieve sustainable growth.
This leads us to a deeper look at what ISO 27001 and ISMS really mean for businesses in Singapore.

(Image Source: Google Gemini)
What Is ISO 27001 and ISMS?
At its core, ISO/IEC 27001 is the leading international standard for establishing, implementing, and continually improving an Information Security Management System (ISMS).
- ISMS meaning: An ISMS is a structured information security framework of policies, processes, and technical controls designed to protect data from threats. It helps organisations move towards ISMS certification, proving compliance with global best practices
- ISMS ISO 27001: The standard defines how an ISMS system should be built, operated, and continually improved. It provides guidance for conducting an ISMS audit to validate effectiveness
(Image Source: ISO 27001 Standard )
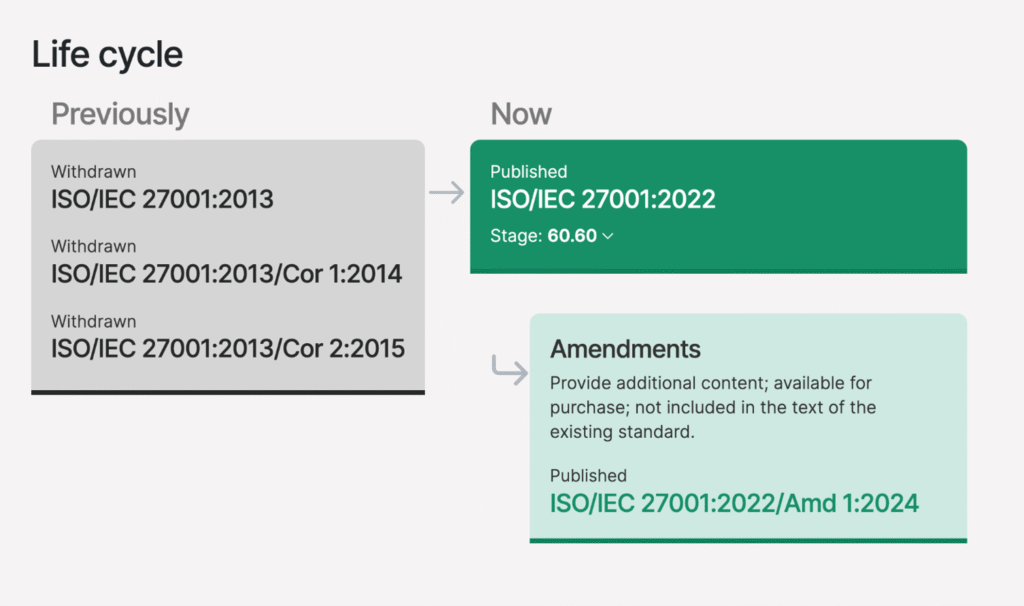
- ISO 27001:2013 vs 2022: The 2022 version lowered the number of controls from 114 to 93 and introduced new ones for cloud security, threat intelligence, and data privacy
- Lifecycle: The ISMS lifecycle follows a continuous improvement loop: Plan → Implement → Monitor → Improve, often referred to in practice as the ISMS PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle
Why ISO 27001 is Important for SMEs, SMBs, and Startups
For SMEs, SMBs, and startups in Singapore, ISO 27001 certification goes beyond compliance; it’s a strategic investment that delivers measurable business value.
- Win larger contracts, including with enterprises and government agencies
- Demonstrate compliance with PDPA and sector-specific regulations
- Build stronger trust with investors, partners, and customers
- Improve operational resilience against cyber incidents and disruptions
- Achieve long-term savings by preventing costly breaches
ROI insight: According to IBM, the average value of a data breach reached USD 4.45 million in 2023. In Singapore, the PDPC fined Ezynetic Pte. Ltd. SGD 17,500 in 2025 after a ransomware-related breach affecting 190,589 individuals, whose personal data was exfiltrated and sold on the dark web. Certification helps SMEs win contracts, access funding, and demonstrate compliance, making it a high-ROI investment despite the initial setup costs, especially when compared to the heavy financial and reputational damage of breaches.
How ISO 27001 Protects Data, Builds Trust, and Improves Resilience
Becoming ISO27001 certified is more than a compliance exercise. It directly addresses what ISO 27001 covers: safeguarding sensitive data, enforcing access controls, and embedding risk management across the organisation. By doing so, the standard helps protect businesses from data breaches, reputational harm, and regulatory penalties.
For SMEs and startups, this means:
- Protecting what matters most: ISO 27001 helps the business to protect customer data, intellectual property, and financial information
- Building trust: Clients, partners, and regulators view certification as proof of maturity and reliability
- Operational resilience: The standard strengthens incident response, continuity planning, and recovery capabilities, ensuring the business can withstand disruptions
Key Components of ISO 27001
To understand the standard, it helps to look at its structure and how each element works together as part of the ISO 27001 process:
- ISO 27001 clauses (4–10): Cover the scope of the ISMS, leadership commitment, planning, support, operations, performance evaluation, and continual improvement
- ISO 27001 Annex A controls (93 in the 2022 version): Provide a practical ISO 27001 checklist of safeguards, including access management, cloud services, supplier security, and incident response
- Risk management: Central to the ISMS, ensuring that every ISO 27001 control is tied to identified risks and applied proportionately
Singapore’s EnterpriseSG actively encourages businesses to adopt ISO 27001 together with ISO 27701 for privacy management, showing its importance at the national level.
How ISO 27001 Certification Works
If you are wondering how ISO 27001 works, here’s the step-by-step process from gap assessment to final certification:
- Gap Assessment – Identify where your business stands versus the ISO 27001 requirements
- ISMS Scope & Policy – Define the scope of your ISMS, document policies, and secure leadership support
- Risk Assessment & Treatment – Identify threats, rate risks, and apply appropriate ISO 27001 controls
- Implementation – Roll out policies, training, monitoring, and technical safeguards
- Internal Audit – Conduct an ISMS audit to test effectiveness before the external review
- Certification Audit – An accredited certification body validates compliance and issues the certificate
ISO 27001 Implementation Guide for SMEs & Startups
Following a structured ISO 27001 implementation guide ensures SMEs and startups avoid delays and audit failures. The process can be broken into practical ISO 27001 implementation steps:
- Project planning – Define objectives, assign responsibilities, and build a timeline. Many organisations use an ISO 27001 implementation project plan XLS to manage tasks, milestones, and resources
- Roadmap development – Create an ISO 27001 implementation roadmap to align with business priorities and allocate resources effectively
- Documentation – Prepare policies, procedures, and records as part of your ISO 27001 implementation plan, ensuring all requirements are addressed
- Implementation checklist – Use an ISO 27001 implementation checklist to track progress, from access controls to incident management
- Monitoring & review – Regularly evaluate performance, collect evidence, and adjust processes for continual improvement
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Even with a solid plan, SMEs often face challenges such as:
- Treating ISO 27001 implementation as an IT-only project rather than an organisation-wide initiative
- Copy-pasting generic templates instead of tailoring them to the specific ISMS framework of the business
- Ignoring evidence collection until the last minute which makes audits more difficult
By following a clear ISO 27001 implementation guide and avoiding these pitfalls, businesses can streamline the journey to certification. To make that journey even easier, many SMEs choose to work with an experienced ISO 27001 consultant who can provide hands-on guidance and ensure audit success.
How to Select the Right ISO Consultant for Your Business
While some SMEs attempt DIY implementation, working with an experienced ISO 27001 consultant in Singapore is often the faster and safer route. A trusted partner can simplify the process, reduce the risk of audit failure, and ensure that your ISMS is tailored to your business needs.
A professional ISO 27001 consultancy typically offers:
- Gap assessments and risk workshops – Identify weaknesses and create a practical roadmap
- Documentation and ISMS policy drafting – Support in preparing an audit-ready ISO 27001 implementation plan
- Internal audits and readiness checks – Independent reviews to strengthen compliance
- Certification preparation and liaison – Connecting with external certification bodies and ensuring all audit requirements are met
At Artan Consulting, we specialise in ISO 27001 consulting services in Singapore and across Asia. Unlike general consultancies, our approach is highly practical and supportive, offering true hand-holding at every stage, from ISO 27001 implementation advisory services to readiness checks and direct support during certification audits. We also leverage our strong relationships to help SMEs communicate smoothly with external certification bodies, removing unnecessary roadblocks.
With our proven methodology and dedicated guidance, Artan ensures your organisation is not only audit-ready but also builds a sustainable ISMS framework that strengthens long-term resilience and confidence in your security posture.
Final Words
ISO 27001 certification goes beyond meeting compliance requirements; it is a foundation for lasting trust, operational resilience, and business growth in Singapore’s competitive landscape. With increasing regulatory expectations and rising cyber threats, SMEs cannot afford to take chances. At Artan Consulting, we provide tailored advisory, ready-to-use templates, and end-to-end guidance, including coordination with certification bodies. By partnering with us, you accelerate compliance, reduce costs, and strengthen your organisation’s ability to thrive securely in the digital economy.
FAQ Clarity
- How does ISO 27001 work in practice for SMEs and startups?
- It provides a structured ISO 27001 process that guides organisations from planning and implementation to monitoring, auditing, and continual improvement.
- How does ISO 27001 certification work with other frameworks?
- Many organisations align their ISMS with ISO 27001 certification work while also referencing NIST, CSA, or MAS TRM guidelines for industry-specific compliance.
- What does ISO 27001 stand for in business value?
- Beyond being a standard, it stands for trust, security, and operational resilience, helping companies win contracts and meet regulatory demands.
- What is the difference between ISO 31000 and ISO 27001 when it comes to risk?
- ISO 31000 is broader, covering enterprise-wide risk management, while ISO 27001 zooms in on information security risks specifically.
- How do ISO 22301 and ISO 27001 differ when it comes to resilience planning?
- ISO 22301 ensures businesses can continue operating during disruptions (continuity), while ISO 27001 helps the business strengthen its ability to withstand disruptions..
- How does ISO 27001 define an asset for protection?
- An asset includes data, IT systems, processes, people, and facilities, anything that has value to the business.

